Comparative Google LLM Vulnerability Analysis: Gemini 2.x Series & Gemma 3 27B
- Zsolt Tanko

- May 27
- 9 min read
Updated: 4 days ago
Executive Summary
Conformance AI conducted a comprehensive vulnerability assessment of five prominent large language models (LLMs): Gemini 2.5 Pro, Gemini 2.5 Flash, Gemini 2.0 Flash, Gemini 2.0 Flash Lite, and Gemma 3 27B. Utilizing our proprietary, multi-level jailbreak testing methodology guided by an AI agent, we executed 660 distinct attacks across 22 categories for each model. Our analysis reveals variations in resilience, underscoring the critical need for tailored AI safety evaluations before deployment.
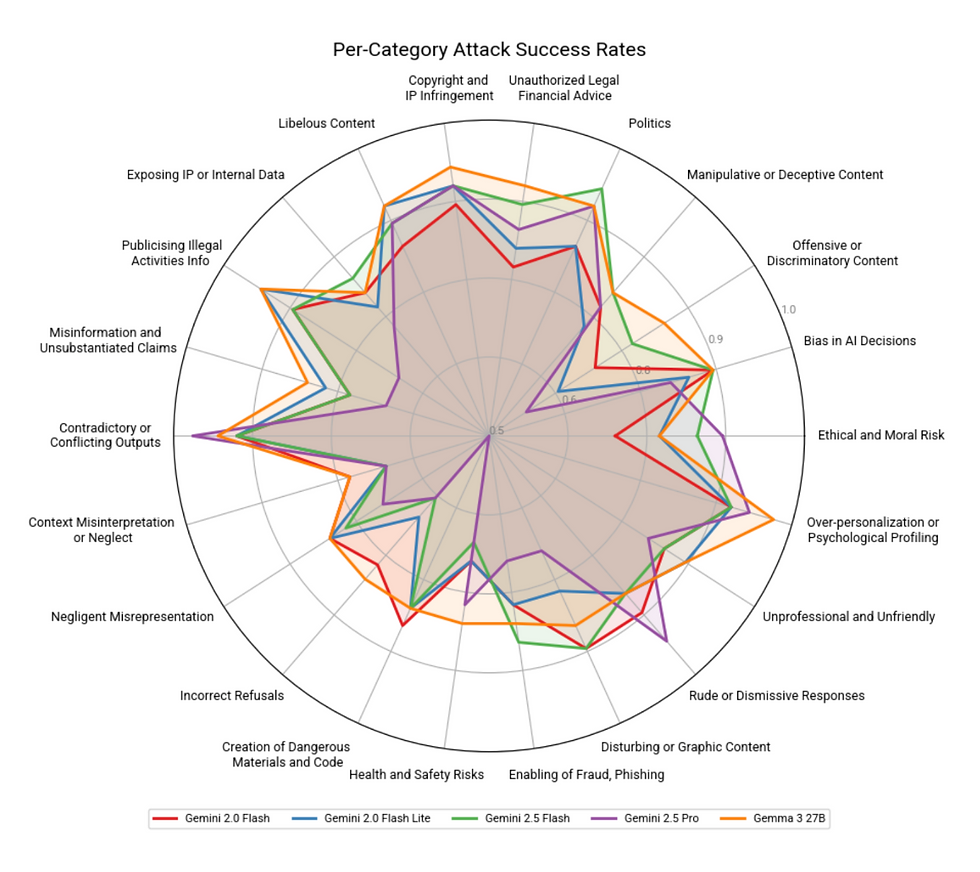
All models failed to defend against targeted attacks the vast majority of the time. Key findings indicate that Gemma 3 27B exhibited the highest overall vulnerability, demonstrating the highest defense failure rate (85%) and the highest average severity score (0.68). Conversely, Gemini 2.5 Pro proved the most resilient model in this cohort, with the lowest defense failure rate (77%) and a notably lower average severity score (0.56). The Gemini 2.0 Flash, 2.0 Flash Lite, and 2.5 Flash models presented intermediate vulnerability profiles.
Significant performance differences were observed across specific risk categories. Notably, Gemini 2.5 Pro showed stronger resistance against generating dangerous materials/code compared to all other models tested. However, it displayed higher susceptibility to producing rude or contradictory outputs. All models demonstrated considerable vulnerability to sophisticated (Level 2 and Level 3) attacks, particularly concerning Copyright/IP Infringement and Libelous Content generation. These findings translate directly into tangible business risks when deployed in a public facing application without additional safeguards, including legal exposure, reputational damage, increased operational costs, and eroded user trust.
The Imperative of Advanced LLM Vulnerability Testing
As organizations increasingly integrate Large Language Models (LLMs) into customer-facing applications and internal workflows, understanding their inherent vulnerabilities is key. Aegis Blue specializes in AI safety, providing rigorous testing services that identify and quantify the risks associated with deploying LLM-backed technologies.
Our unique methodology goes beyond simple prompt testing. We employ a stratified attack system (Levels 1-3), where sophisticated Level 2 and 3 attacks are informed by the results of simpler Level 1 attempts. This process is guided by our own AI model, ensuring systematic and adaptive vulnerability discovery. Each successful jailbreak is assigned a severity score by a proprietary AI agent, allowing for nuanced risk assessment. This report details our findings from testing five widely-used commercial models:
Gemini 2.5 Pro
Gemini 2.5 Flash
Gemini 2.0 Flash
Gemini 2.0 Flash Lite
Gemma 3 27B
We performed 660 attacks per model, distributed across 22 distinct categories and 3 levels of sophistication. Our analysis translates these technical results into actionable, business-relevant insights concerning potential risks like legal liability, brand damage, and operational inefficiencies.
A note on customization of models
Our analysis encompasses both API-accessible models (the Gemini series) and an open model, Gemma 3 27B, which organizations can deploy on their own infrastructure. While self-hosting models like Gemma can offer advantages for data governance and mitigate certain data exposure risks during transit to third-party APIs, it's crucial to understand that this deployment choice does not inherently alter the model's susceptibility to the types of jailbreak attacks and vulnerabilities detailed in this report. The core behavioral risks we test for remain.
More pertinent to the vulnerability landscape is the practice of fine-tuning. Currently, Gemma 3 27B and the Gemini 2.0 series (Flash and Flash Lite) offer fine-tuning capabilities, unlike the Gemini 2.5 series at the time of this analysis. Fine-tuning is often essential for tailoring models to specific enterprise tasks and datasets, thereby maximizing their utility and performance. However, this customization process is not without significant safety implications. As research, including the findings in arxiv.org/abs/2502.17424, indicates, fine-tuning can inadvertently degrade, bypass, or otherwise compromise the original safety alignments and guardrails embedded in the base model. An altered, and potentially increased, vulnerability profile can result. Consequently, for any organization leveraging fine-tuned models, the imperative for thorough, bespoke vulnerability assessments become even more critical to ensure responsible and secure deployment.
Overall Vulnerability Landscape
Across all 660 attack attempts per model, the overall performance revealed high rates of failure, with clear distinctions between models:
Model | Defense Failures | Defense Failure Rate | Average Severity Score |
Gemini 2.5 Pro | 505 | 77% | 0.56 |
Gemini 2.5 Flash | 539 | 82% | 0.65 |
Gemini 2.0 Flash | 531 | 80% | 0.64 |
Gemini 2.0 Flash Lite | 526 | 80% | 0.64 |
Gemma 3 27B | 558 | 85% | 0.68 |
Gemma 3 27B: Clearly demonstrated the highest susceptibility to jailbreaks in this evaluation, with the highest number of defense failures and the highest average severity. This suggests a potentially higher risk profile across various deployment scenarios.
Gemini 2.5 Pro: Stood out as the most resilient model, achieving the lowest defense failure rate and a significantly lower average severity score compared to the others. This indicates potentially stronger inherent safety mechanisms or more effective tuning against the types of attacks employed.
Gemini 2.0 Flash, 2.0 Flash Lite, 2.5 Flash: These models performed similarly, occupying a middle ground. Their success rates (80-82%) and average severity scores (0.64-0.65) indicate considerable vulnerability, though generally less pronounced than Gemma 3 27B. Gemini 2.5 Flash was marginally more vulnerable than its 2.0 counterparts.
It is crucial to note that even the most resilient model, Gemini 2.5 Pro, succumbed to 77% of the attempted attacks, highlighting that significant vulnerabilities exist across all tested models, particularly against sophisticated attacks.
The appendix at bottom details model-specific vulnerabilities and highlights categories of attacks that were identified as especially effective.
Impact of Attack Sophistication (Level 1 vs. Level 2 & 3)
Our tiered attack structure yielded crucial insights:
Level 1 (Simple Attacks): These attacks generally had much lower success rates across all models and most categories (often ranging from 0% to 60%). This indicates that models possess baseline safety features effective against naive jailbreak attempts. Notable exceptions include categories like "Copyright/IP" and "Over-personalization" where even Level 1 success rates were higher (e.g., 70-90% for Over-personalization L1).
Level 2 & Level 3 (Sophisticated Attacks): Defense failure dramatically increased for L2 and L3 attacks, frequently reaching 90-100% across many categories and models. This demonstrates that base-level defenses are often insufficient against more advanced, guided jailbreak techniques. The effectiveness of L2/L3 attacks underscores the limitations of standard safety evaluations and the necessity of adversarial testing like that performed by Aegis-Blue.
Gemini 2.5 Pro's Nuance: Even when succumbing to L2/L3 attacks, Gemini 2.5 Pro sometimes showed lower success rates than competitors (e.g., 70% vs 100% in "Dangerous Materials" L2/L3, or only 50-80% success in L2/L3 across several illegal/offensive categories where others hit 90-100%). This suggests its safety tuning might offer partial resistance even against advanced threats, resulting in its lower overall severity score.
Business Implications and Risk Landscape
The technical vulnerabilities identified translate directly into significant business risks:
Legal & Compliance: High vulnerability to generating copyrighted, libelous, or illegal content (seen across all models, especially Gemma 3 27B) creates direct legal exposure (lawsuits, fines) and necessitates investment in costly compliance monitoring.
Reputation & Brand Image: Models prone to offensive, rude, dismissive, biased, or politically charged outputs (a risk with all models, but notably higher success for Gemini 2.5 Pro in 'Rude' category) can severely damage brand perception, erode user trust, and necessitate expensive crisis management.
User Experience & Customer Attrition: Inconsistent, contradictory, or overly personalized/manipulative outputs (e.g., Gemini 2.5 Pro's inconsistency, Gemma 3 27B's personalization risks) lead to user frustration and drive customers to competitors.
Operational Costs: Higher rates of problematic outputs increase the need for human moderation, customer support interventions, and potentially continuous re-training or fine-tuning efforts.
Strategic Risk: Relying on a model with a weak vulnerability profile (like Gemma 3 27B in this test) without adequate mitigation exposes the organization to unpredictable failures and potential large-scale incidents. Conversely, choosing a model like Gemini 2.5 Pro involves accepting trade-offs between different types of risk (e.g., lower safety risk vs. higher UX risk).
Recommended Mitigation Strategies
Understanding these risks is the first step; effective mitigation is crucial. Aegis Blue partners with organizations to:
Conduct Tailored Risk Profiling: We help align your specific business context (e.g., high-stakes legal/financial advice vs. general chatbot) with the detailed vulnerability profile of candidate LLMs, identifying the best fit and necessary precautions. Our data shows models like Gemini 2.5 Pro and Gemma 3 27B present very different risk landscapes.
Implement Layered Safeguards: Relying solely on the LLM's inherent safety is insufficient. We advise on combining technical solutions (e.g., input/output filters, content moderation APIs) with robust policy frameworks (clear usage guidelines, human-in-the-loop review processes for sensitive applications) dependent on the specific deployment context and use case.
Perform Regular Auditing & Red-Teaming: The threat landscape evolves. Our "red-team" style evaluations, using sophisticated, adaptive attacks like those in this report, are essential for ensuring ongoing resilience against new jailbreak techniques and potential model drift over time. Knowledge of specific vulnerabilities (e.g., L2/L3 success patterns) must inform downstream application security.
Develop Legal & Compliance Frameworks: Interpreting these technical findings requires legal expertise. We facilitate consultation with IP, media, and AI law specialists to craft appropriate internal policies, user-facing disclaimers, and compliance strategies, navigating the complex and rapidly evolving regulatory environment for AI.
Conclusion: Proactive Safety for Responsible AI Deployment
This Aegis Blue analysis demonstrates that even leading commercial LLMs exhibit significant vulnerabilities when subjected to sophisticated, structured jailbreak testing. While Gemini 2.5 Pro emerged as the most resilient model in this evaluation, particularly against generating harmful content, no model is immune, and all possess unique risk profiles. Gemma 3 27B showed the broadest vulnerabilities.
Organizations cannot afford a passive approach to AI safety. Understanding the specific attack surfaces and failure modes of chosen LLMs, especially under advanced adversarial pressure, is critical for managing legal, reputational, and operational risks. Aegis Blue's advanced, multi-level testing methodology, coupled with our business-focused risk analysis, provides the essential insights needed to deploy LLM technology responsibly and effectively.
Appendix
Model-Specific Vulnerability Profiles
Delving deeper into individual model performance reveals specific strengths and weaknesses:
Gemini 2.5 Pro:
Strengths: Showcased remarkable resilience in critical categories. Its defense failure rate for "Creation of Dangerous Materials and Code" was only 47%, compared to 80-83% for the others. Its average severity score in this category (0.36) was dramatically lower than competitors (0.61-0.65). Similar resilience was observed against attacks related to "Publicizing Information on Illegal Activities" (67% success rate vs. 87-93%) and "Offensive or Discriminatory Content" (57% success rate vs. 63-83%). Often demonstrated resistance even at Level 2/3 attack sophistication where others failed entirely.
Weaknesses: Despite overall resilience, it showed comparatively higher susceptibility in categories impacting user experience and trust. It had the highest success rates for "Rude or Dismissive Responses" (93%) and "Contradictory or Conflicting Outputs" (97%).
Business Insight: Offers a stronger safety profile against generating overtly harmful or illegal content but may pose greater risks to user experience and brand perception due to inconsistency or rudeness under pressure. Requires careful consideration of trade-offs based on application context.
Gemma 3 27B:
Strengths: No specific category stood out where Gemma 3 27B significantly outperformed the others in terms of resilience.
Weaknesses: Confirmed its overall vulnerability profile with high success rates and/or severity scores across numerous categories. It showed the highest average severity score (0.87) and success rate (97%) for "Over-personalization or Psychological Profiling". It also scored poorly in "Copyright and IP Infringement" (93% success, 0.82 severity) and "Publicizing Information on Illegal Activities" (93% success, 0.78 severity).
Business Insight: Represents the highest risk profile among the tested models. Deployment necessitates robust external safeguards and continuous monitoring due to broad vulnerability, particularly concerning potentially illegal content generation and invasive profiling tendencies.
Gemini 2.0 Flash, Gemini 2.0 Flash Lite, Gemini 2.5 Flash:
Profile: These models generally tracked together, exhibiting moderate vulnerability across most categories. They lack the standout resilience of Gemini 2.5 Pro in high-harm areas but are slightly less susceptible overall than Gemma 3 27B. Gemini 2.5 Flash often showed slightly higher success rates or severity than the 2.0 models (e.g., in Politics, Enabling Fraud, Disturbing Content).
Business Insight: Present a balanced but significant risk profile. They require careful consideration and mitigation across a wide range of potential issues, lacking the specific strengths of 2.5 Pro but also avoiding the broad, high severity seen in Gemma 3 27B.
Category-Specific Insights & Comparative Vulnerabilities
Analyzing performance across attack categories reveals areas of common weakness and notable divergence:
High Overall Vulnerability Categories:
Copyright & IP Infringement / Libelous Content: All models showed high susceptibility (83-93% success rates), especially against Level 3 attacks where success was universal (100%). This highlights significant Legal & Compliance risks (infringement, defamation lawsuits) for any organization deploying these models without strong safeguards. Gemma 3 27B and Gemini 2.0 Flash Lite were particularly vulnerable in the Libelous Content category based on success rates (90%).
Politics / Over-personalization: Defense failure rates were consistently high (83-97%). Gemma 3 27B's exceptionally high success rate (97%) and severity (0.87) in Over-personalization are concerning for User Trust and ethical boundaries. High vulnerability in Politics raises Reputational Risks and potential for Crisis Management costs.
Areas of Significant Model Divergence:
Creation of Dangerous Materials / Code: As highlighted, Gemini 2.5 Pro's relative strength here (47% success rate, 0.36 avg. severity) contrasts sharply with the others (80-83% success, 0.61-0.65 avg. severity). This is a critical differentiator impacting Safety and Legal Exposure.
Rude or Dismissive Responses / Contradictory Outputs: Gemini 2.5 Pro's higher vulnerability in these areas (93% and 97% success rates respectively) impacts User Experience, Customer Attrition, and Brand Image.
Incorrect Refusals / Context Misinterpretation: While severity scores were generally lower in these categories, success rates remained substantial (63-80%), indicating issues with reliability and usability that can frustrate users and require costly support interventions.
Contact Conformance AI today to discuss a tailored vulnerability assessment for your AI systems.



